Use Cases
Kore has been designed with traceability use cases in mind. It is considered that in these use cases the vast majority of events are unilateral, which allows taking advantage of Kore’s differentiating features, such as ledger single ownership model. Some Kore technology use cases will be presented as examples to facilitate understanding.
Processes
Any process that requires traceability with high levels of security and confidence, is apt to be a suitable use case to be traced through Kore nodes, for instance, the water cycle. This process describes how the flow of water starts from a point A and passes through a series of other points until it finally returns to the point of origin, simulating a circular path. Along the way, the water flow passes through various entities and processes that cause its volume to decrease. Simultaneously, at some of these points it is possible to analyze the state of that flow by means of sensors or other systems that allow to obtain and generate additional information of the flow itself.
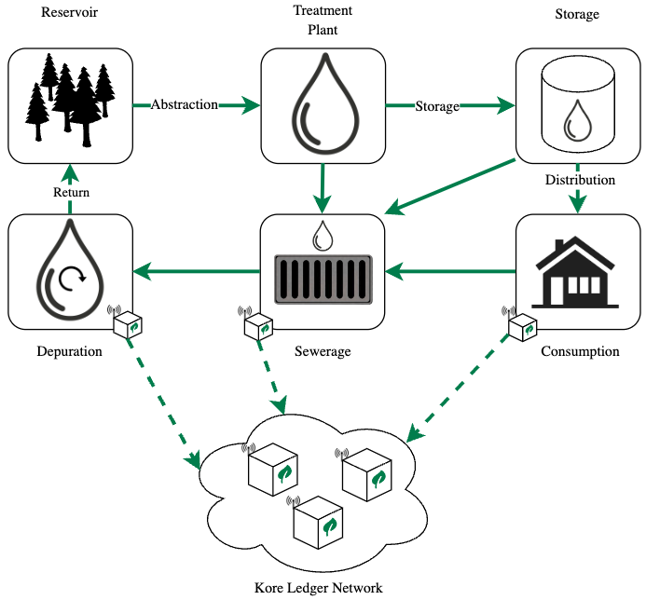
Figure 1: Water cycle with Kore Ledger.
Iot
IoT is defined as The Internet of things. The Internet of things describes physical objects (or groups of such objects) with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communications networks. For example, the smart city concept has recently been gaining momentum.
Today, the benefits of a city are not only limited to physical infrastructure, services and institutional support, but also to the availability and quality of communication channels, and the transmission and exploitation of knowledge from these channels to improve and efficiently provide resources to social infrastructures.
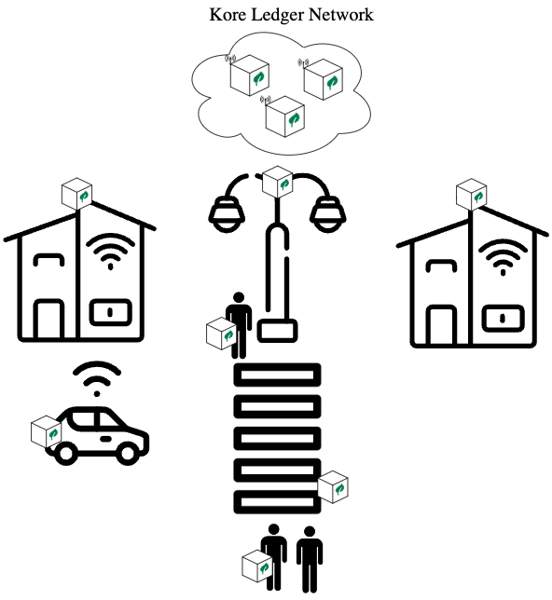
Figure 2: Smart City connected to Kore Ledger Network.
One of the most interesting processes within a smart city, both for its public health implications and its economic nature, is waste management. The first step is to collect the garbage provided by citizens in containers which have sensors or other systems that determine the weight of the container and how full they are. Once the sensor is activated at the value set by the company, the garbage truck picks up the container to take it to the recycling factory, where they are responsible for separating these elements and perform the relevant processes for recycling. Finally, when the process is finished, these materials are put back on sale so that they can be used again and the process explained above is repeated.
Beef Traceability
Beef is a common product in supermarkets and its traceability is crucial to guarantee its quality, safety and origin. With Kore, you can implement a traceability system for beef from field to table by following these steps:
- Livestock Breeding and Feeding: The system begins with the raising and feeding of livestock on farms. Kore can record information about where cattle come from, their genetics, diet, husbandry conditions and health. Data may include diet type (organic, conventional), medication use, and other important details.
- Slaughter and Processing: When cattle are slaughtered, Kore records process data, including quality controls, date and location of slaughter. During processing, meat cuts and by-products can be tracked, ensuring traceability of each piece.
- Transportation and Storage: Kore allows tracking of meat during transportation from the processing plant to distribution centers and stores. Transport conditions, such as temperature, can be monitored to ensure the meat remains in optimal condition.
- Distribution to Supermarkets: Once the meat reaches supermarkets, Kore can record data on its storage, rotation and display on shelves. Retailers can access detailed information about the origin of meat and its characteristics, allowing them to make informed sales decisions.
- Sale to the Final Consumer: Consumers can access traceability information through QR codes or labels on the meat packaging. This allows them to know the origin of the meat, its quality history and any other relevant information.
This level of traceability ensures that consumers receive high-quality beef and that food safety standards are met. Additionally, it helps prevent fraud and quickly identify problems in the event of foodborne illness outbreaks.